一、整理原因:
为了辅助理解无障碍google官方开发文档api的原理。
二、参考文档
三、无障碍服务框架结构分析
3.1.结构
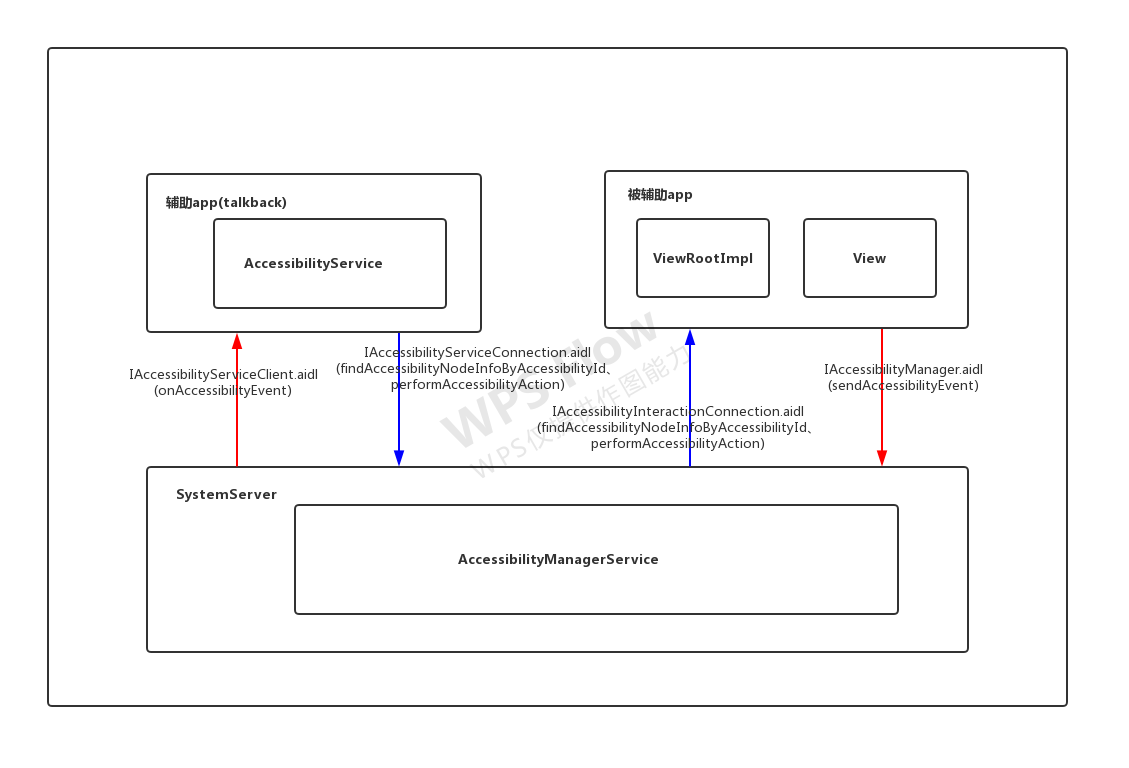
3.2、相关类图

整个talkback机制涉及了4个进程,SystemServer(蓝色部分)、Talkback(黄色部分)、被辅助app进程(绿色部分),TTS引擎进程(暂不分析)
四个AIDL接口,图上红色部分
3.2.1、talkback(辅助app,实现了AccessibilityService的app)
辅助app需要用到的在framewors目录中相关的类,主要是继承AccessibilityService从而接收SystemServer进程发送过来的无障碍事件并进行相关处理

3.2.2、被辅助app进程(被辅助app)
被辅助的app的无障碍特性主要是通过扩展Android的View框架的功能对外提供,因此无障碍相关的类主要放在view包中,如下。

3.2.3、system_process
SystemServer进程中的无障碍服务管理类如下所示,比如核心的AccessibilityManagerService,用于协调辅助app进程和被辅助app进程的交互;TouchExpolorer用于实现“触摸浏览”手势功能等。
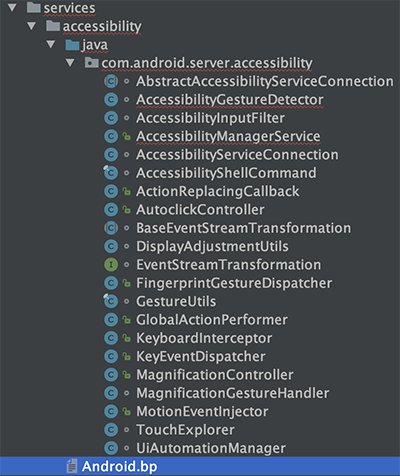
系统进程SystemServer中的AccessibilityManagerService,用来管理所有的无障碍服务,类似AMS,SystemServer启动时会在startOtherServices方法中启动AccessibilityManagerService,startOtherServices方法在ActivityManagerService、PackageManagerService等一些核心服务的后面启动。
com.android.server.SystemServer.java
/**
* Starts a miscellaneous grab bag of stuff that has yet to be refactored
* and organized.
*/
private void startOtherServices() {
...
traceBeginAndSlog("StartAccessibilityManagerService");
try {
ServiceManager.addService(Context.ACCESSIBILITY_SERVICE,
new AccessibilityManagerService(context));
} catch (Throwable e) {
reportWtf("starting Accessibility Manager", e);
}
traceEnd();
...
}
3.3.4、TTS

暂不分析
3.3 无障碍框架AIDL接口
理解无障碍框架的aidl的设计是理解无障碍框架的关键。
我们进行无障碍的开发通常会涉及到三个进程:
辅助app(talkback、或者我们自己开发的无障碍应用(比如红包助手))
SystemServer(系统服务进程,管理所有的无障碍服务,并且起到中转的作用,类似AMS的设计)
被辅助的app()
跨进程通信需要用到aidl接口,无障碍服务框架也不例外,由于涉及到三个进程的通信,并且辅助app通常不需要直接跟被辅助的app通信,大部分通过SystemServer进行中转通信,因此主要涉及到了四个aidl接口:
被辅助app->SystemServer(IAccessibilityManager.aidl)
SystemServer->辅助app(IAccessibilityServiceClient.aidl)
辅助app->SystemServer(IAccessibilityServiceConnection.aidl)
SystemServer->被辅助app(IAccessibilityInteractionConnection.aidl)
3.3.1、IAccessibilityManager.aidl(客户端:被辅助app、服务端:SystemServer)
比如当被辅助app产生触摸事件后,会通过这个接口发送无障碍事件给SystemServer进程的AccessibilityManagerService
android.view.accessibility.IAccessibilityManager.aidl
/**
* Interface implemented by the AccessibilityManagerService called by
* the AccessibilityManagers.
*
* @hide
*/
interface IAccessibilityManager {
oneway void sendAccessibilityEvent(in AccessibilityEvent uiEvent, int userId);
long addClient(IAccessibilityManagerClient client, int userId);
List<AccessibilityServiceInfo> getInstalledAccessibilityServiceList(int userId);
List<AccessibilityServiceInfo> getEnabledAccessibilityServiceList(int feedbackType, int userId);
int addAccessibilityInteractionConnection(IWindow windowToken,
in IAccessibilityInteractionConnection connection,
String packageName, int userId);
void removeAccessibilityInteractionConnection(IWindow windowToken);
void notifyAccessibilityButtonClicked();
// Requires WRITE_SECURE_SETTINGS
void performAccessibilityShortcut();
}
3.3.2 、IAccessibilityServiceClient.aidl(客户端:SystemServer、服务端:辅助app)
当SystemServer接收到被辅助的app发送的无障碍事件时,会将事件通过该接口传递给辅助app进程进行处理。
android.accessibilityservice.IAccessibilityServiceClient.aidl
/**
* Top-level interface to an accessibility service component.
*/
oneway interface IAccessibilityServiceClient {
void onAccessibilityEvent(in AccessibilityEvent event, in boolean serviceWantsEvent);
void onSoftKeyboardShowModeChanged(int showMode);
void onPerformGestureResult(int sequence, boolean completedSuccessfully);
void onAccessibilityButtonClicked();
void onAccessibilityButtonAvailabilityChanged(boolean available);
...
}
3.3.3、IAccessibilityServiceConnection.aidl(客户端:辅助app、服务端:SystemServer)
当我们需要找到被辅助的app的某个view的信息时,可以通过该接口的findAccessibilityNodeInfosByViewId方法实现。
android.accessibilityservice.IAccessibilityServiceConnection.aidl
/**
* Interface given to an AccessibilitySerivce to talk to the AccessibilityManagerService.
*/
interface IAccessibilityServiceConnection {
String[] findAccessibilityNodeInfoByAccessibilityId(int accessibilityWindowId,
long accessibilityNodeId, int interactionId,
IAccessibilityInteractionConnectionCallback callback, int flags, long threadId,
in Bundle arguments);
String[] findAccessibilityNodeInfosByViewId(int accessibilityWindowId,
long accessibilityNodeId, String viewId, int interactionId,
IAccessibilityInteractionConnectionCallback callback, long threadId);
String[] findFocus(int accessibilityWindowId, long accessibilityNodeId, int focusType,
int interactionId, IAccessibilityInteractionConnectionCallback callback, long threadId);
boolean performAccessibilityAction(int accessibilityWindowId, long accessibilityNodeId,
int action, in Bundle arguments, int interactionId,
IAccessibilityInteractionConnectionCallback callback, long threadId);
AccessibilityServiceInfo getServiceInfo();
boolean performGlobalAction(int action);
boolean isAccessibilityButtonAvailable();
}
3.3.4、IAccessibilityInteractionConnection.aidl(客户端:SystemServer、服务端:被辅助app)
android.view.accessibility.IAccessibilityInteractionConnection.aidl
/**
* Interface for interaction between the AccessibilityManagerService
* and the ViewRoot in a given window.
*
* @hide
*/
oneway interface IAccessibilityInteractionConnection {
void findAccessibilityNodeInfoByAccessibilityId(long accessibilityNodeId, in Region bounds,
int interactionId, IAccessibilityInteractionConnectionCallback callback, int flags,
int interrogatingPid, long interrogatingTid, in MagnificationSpec spec,
in Bundle arguments);
...
void findFocus(long accessibilityNodeId, int focusType, in Region bounds, int interactionId,
IAccessibilityInteractionConnectionCallback callback, int flags, int interrogatingPid,
long interrogatingTid, in MagnificationSpec spec);
...
void performAccessibilityAction(long accessibilityNodeId, int action, in Bundle arguments,
int interactionId, IAccessibilityInteractionConnectionCallback callback, int flags,
int interrogatingPid, long interrogatingTid);
}
四、流程分析
4.1、AccessibilityService启动流程(以talkback开关打开后到TalkbackService启动进行分析)。
在设置中打开talback开关后,会调用到如下方法,最终会往Settings provider中key为Settings.Secure.ENABLED_ACCESSIBILITY_SERVICES的字段写入Talkback注册的AccessibilityService值(TalkbackService),这个值保存在
/data/system/users/0/settings_secure.xml文件中。(其他app的AccessibilityService也保存在同一个key中)
com.android.settingslib.accessibility.AccessibilityUtils.java
/**
* Changes an accessibility component's state for {@param userId}.
*/
public static void setAccessibilityServiceState(Context context, ComponentName toggledService,
boolean enabled, int userId) {
...
Settings.Secure.putStringForUser(context.getContentResolver(),
Settings.Secure.ENABLED_ACCESSIBILITY_SERVICES,
enabledServicesBuilder.toString(), userId);
}
由于AccessibilityManagerService创建时注册了AccessibilityContentObserver,因此马上会收到Settings provider数据变化的监听。
com.android.server.accessibility.AccessibilityServiceConnection.java
private void updateServicesLocked(UserState userState) {
...
if (userState.mEnabledServices.contains(componentName)
&& !mUiAutomationManager.suppressingAccessibilityServicesLocked()) {
if (service == null) {
service = new AccessibilityServiceConnection(userState, mContext, componentName,
installedService, sIdCounter++, mMainHandler, mLock, mSecurityPolicy,
this, mWindowManagerService, mGlobalActionPerformer);
}
...
service.bindLocked();
} ...
}
...
updateAccessibilityEnabledSetting(userState);
}
根据获取到的AccessibilityService信息(com.google.android.marvin.talkback/com.google.android.marvin.talkback.TalkBackService)创建出AccessibilityServiceConnection。AccessibilityServiceConnection代表了一个无障碍服务,存储用于管理这个服务需要的所有数据,提供了开始/停止服务和在服务管理的数据结构中添加或者移除这个服务的api。
接着调用bindServiceAsUser方法来绑定服务。
com.android.server.accessibility.AccessibilityServiceConnection.java
public void bindLocked() {
...
try {
...
if (mService == null && mContext.bindServiceAsUser(
mIntent, this, flags, new UserHandle(userState.mUserId))) {
userState.getBindingServicesLocked().add(mComponentName);
}
} ...
}
服务启动后会跨进程调用到TalkbackService(AccessibilityService)的onBind方法
android.accessibilityservice.AccessibilityService
/**
* Implement to return the implementation of the internal accessibility
* service interface.
*/
@Override
public final IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return new IAccessibilityServiceClientWrapper(this, getMainLooper(), new Callbacks() {
@Override
public void onServiceConnected() {
AccessibilityService.this.dispatchServiceConnected();
}
...
@Override
public void onAccessibilityEvent(AccessibilityEvent event) {
AccessibilityService.this.onAccessibilityEvent(event);
}
...
});
}
onBind方法返回的是一个IAccessibilityServiceClientWrapper的binder对象
/**
* Implements the internal {@link IAccessibilityServiceClient} interface to convert
* incoming calls to it back to calls on an {@link AccessibilityService}.
*
* @hide
*/
public static class IAccessibilityServiceClientWrapper extends IAccessibilityServiceClient.Stub
implements HandlerCaller.Callback {
...
private final HandlerCaller mCaller;
private final Callbacks mCallback;
private int mConnectionId = AccessibilityInteractionClient.NO_ID;
public IAccessibilityServiceClientWrapper(Context context, Looper looper,
Callbacks callback) {
mCallback = callback;
mCaller = new HandlerCaller(context, looper, this, true /*asyncHandler*/);
}
public void init(IAccessibilityServiceConnection connection, int connectionId,
IBinder windowToken) {
Message message = mCaller.obtainMessageIOO(DO_INIT, connectionId,
connection, windowToken);
mCaller.sendMessage(message);
}
...
public void onAccessibilityEvent(AccessibilityEvent event, boolean serviceWantsEvent) {
Message message = mCaller.obtainMessageBO(
DO_ON_ACCESSIBILITY_EVENT, serviceWantsEvent, event);
mCaller.sendMessage(message);
}
...
@Override
public void executeMessage(Message message) {
switch (message.what) {
case DO_ON_ACCESSIBILITY_EVENT: {
AccessibilityEvent event = (AccessibilityEvent) message.obj;
boolean serviceWantsEvent = message.arg1 != 0;
if (event != null) {
// Send the event to AccessibilityCache via AccessibilityInteractionClient
AccessibilityInteractionClient.getInstance().onAccessibilityEvent(event);
if (serviceWantsEvent
&& (mConnectionId != AccessibilityInteractionClient.NO_ID)) {
// Send the event to AccessibilityService
mCallback.onAccessibilityEvent(event);
}
...
}
} return;
...
case DO_INIT: {
mConnectionId = message.arg1;
SomeArgs args = (SomeArgs) message.obj;
IAccessibilityServiceConnection connection =
(IAccessibilityServiceConnection) args.arg1;
IBinder windowToken = (IBinder) args.arg2;
args.recycle();
if (connection != null) {
AccessibilityInteractionClient.getInstance().addConnection(mConnectionId,
connection);
mCallback.init(mConnectionId, windowToken);
mCallback.onServiceConnected();
}...
} return;
...
}
}
}
IAccessibilityServiceClientWrapper中保存了一个HandlerCaller和Callbacks对象,其中HandlerCaller主要是将SystemServer进程中AccessibilityServiceConnection的binder call的binder线程调研切换到AccessibilityService的主线程调用。Callbacks对象则将IAccessibilityServiceClientWrapper中的调用回调到AccessibilityService中。
AccessibilityService返回binder后会走到AccessibilityServiceConnection的onServiceConnected调用中:
com.android.server.accessibility.AccessibilityServiceConnection.java
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName componentName, IBinder service) {
synchronized (mLock) {
...
mServiceInterface = IAccessibilityServiceClient.Stub.asInterface(service);
...
userState.addServiceLocked(this);
mSystemSupport.onClientChange(false);
// Initialize the service on the main handler after we're done setting up for
// the new configuration (for example, initializing the input filter).
mMainHandler.sendMessage(obtainMessage(
AccessibilityServiceConnection::initializeService, this));
}
}
private void initializeService() {
IAccessibilityServiceClient serviceInterface = null;
...
try {
serviceInterface.init(this, mId, mOverlayWindowToken);
} catch (RemoteException re) {
...
}
}
在serviceInterface.init方法中(binder调用)将这个AccessibilityServiceConnection、mId和mOverlayWindowToken传给AccessibilityService完成初始化工作。
初始化时会调用
AccessibilityInteractionClient.getInstance().addConnection(mConnectionId,
connection);
将AccessibilityServiceConnection保存到AccessibilityInteractionClient中。
4.2、无障碍模式下视图状态初始化流程。

分析该流程原因:
为了辅助理解如下方法:
getAccessibilityNodeProvider
onInitializeAccessibilityNodeInfo
主要流程分析:
1、talkback打开状态下,新的应用打开时,TalkbackService会接收到类型为TYPE_WINDOWS_CHANGED的无障碍事件,这个事件是SystemServer进程接收到其他进程发出的TYPE_VIEW_ACCESSIBILITY_FOCUSED事件时附带发出的,应用发出TYPE_VIEW_ACCESSIBILITY_FOCUSED事件的流程在下一节分析,暂时跳过。
2、当tailback收到TYPE_WINDOWS_CHANGED事件时,会间接调用调用父类AccessibilityService的getRootInActiveWindow方法,如上图,经过SystemServer进程中转后会调用到DecorView的getAccessibilityNodeProvider,由于DecorView没有重写getAccessibilityNodeProvider方法,因此会调用到View的createAccessibilityNodeInfo方法,进一步会调用到onInitializeAccessibilityNodeInfo方法,如果没有重写该方法,则默认实现在onInitializeAccessibilityNodeInfoInternal中。
3、AccessibilityNodePrefetcher在取出DecorView的无障碍节点后,会进一步通过prefetchDescendantsOfRealNode方法取子view的无障碍节点。同理,如果我们重写了getAccessibilityNodeProvider方法(一些特殊的自定义view需要自己重写该方法,比如webview,android.widget.NumberPicker等),重写getAccessibilityNodeProvider,需要我们实现一个AccessibilityNodeProvider的子类,来实现虚拟的view来支持无障碍模式。通常实现比较复杂的view时会重写这两个方法
4.3、无障碍事件分发流程(重要,app适配无障碍以及处理无障碍相关问题主要通过该流程入手)。
流程:被辅助app将无障碍事件发送给辅助app,systemserver进程作为中转,接口为IAccessibilityManager.aidl和IAccessibilityServiceClient.aidl

分析该流程原因:
为了辅助理解如下方法:
sendAccessibilityEvent
sendAccessibilityEventUnchecked
onInitializeAccessibilityEvent
dispatchPopulateAccessibilityEvent
onPopulateAccessibilityEvent
onRequestSendAccessibilityEvent
由于talkback的无障碍服务中声明了android:canRequestTouchExplorationMode="true”,因此开启talkback后AccessibilityManagerService会更新AccessibilityInputFilter成员变量的触摸浏览(FLAG_FEATURE_TOUCH_EXPLORATION)的特性为true。
com.android.server.accessibility.AccessibilityInputFilter
private void enableFeatures() {
...
if ((mEnabledFeatures & FLAG_FEATURE_TOUCH_EXPLORATION) != 0) {
mTouchExplorer = new TouchExplorer(mContext, mAms);
addFirstEventHandler(mTouchExplorer);
}
...
}
触摸浏览特性开启后会创建一个TouchExplorer对象。AccessibilityInputFilter继承自InputFilter,对输入事件进行过滤,通过和TouchExplorer配合从而实现talkback模式下的触摸浏览手势。
/**
* This class is a strategy for performing touch exploration. It
* transforms the motion event stream by modifying, adding, replacing,
* and consuming certain events. The interaction model is:
*
* <ol>
* <li>1. One finger moving slow around performs touch exploration.</li>
* <li>2. One finger moving fast around performs gestures.</li>
* <li>3. Two close fingers moving in the same direction perform a drag.</li>
* <li>4. Multi-finger gestures are delivered to view hierarchy.</li>
* <li>5. Two fingers moving in different directions are considered a multi-finger gesture.</li>
* <li>7. Double tapping clicks on the on the last touch explored location if it was in
* a window that does not take focus, otherwise the click is within the accessibility
* focused rectangle.</li>
* <li>7. Tapping and holding for a while performs a long press in a similar fashion
* as the click above.</li>
* <ol>
*
* @hide
*/
class TouchExplorer extends BaseEventStreamTransformation
implements AccessibilityGestureDetector.Listener {
...
该类负责将普通的触摸事件转换为触摸浏览手势,比如将MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN事件转换为悬停事件)(MotionEvent.ACTION_HOVER_ENTER)。因此在talkback模式下,当我们点击一次view上的控件时,应用收到的是(ACTION_HOVER_ENTER)事件,而只有双击才会传递我们熟悉的ACTION_DOWN事件
*ViewRootImpl:View层次结构的根。View的绘制流程(测量measure、布局layout、绘制draw)和输入事件的分发流程都是从ViewRootImp开始。
主要流程分析:
1、ViewRootImpl的内部类WindowInputEventReceiver从native方法调起dispatchInputEvent方法。
2、ViewRootImpl调用deliverInputEvent传递事件输入事件。
3、从顶层的DecorView的dispatchPointerEvent开始分发输入事件。
android.view.View.java
/**
* Dispatch a pointer event.
* <p>
* Dispatches touch related pointer events to {@link #onTouchEvent(MotionEvent)} and all
* other events to {@link #onGenericMotionEvent(MotionEvent)}. This separation of concerns
* reinforces the invariant that {@link #onTouchEvent(MotionEvent)} is really about touches
* and should not be expected to handle other pointing device features.
* </p>
*
* @param event The motion event to be dispatched.
* @return True if the event was handled by the view, false otherwise.
* @hide
*/
public final boolean dispatchPointerEvent(MotionEvent event) {
if (event.isTouchEvent()) {
return dispatchTouchEvent(event);
} else {
return dispatchGenericMotionEvent(event);
}
}
...
/**
* Returns true if this motion event is a touch event.
* <p>
* Specifically excludes pointer events with action {@link #ACTION_HOVER_MOVE},
* {@link #ACTION_HOVER_ENTER}, {@link #ACTION_HOVER_EXIT}, or {@link #ACTION_SCROLL}
* because they are not actually touch events (the pointer is not down).
* </p>
* @return True if this motion event is a touch event.
* @hide
*/
public final boolean isTouchEvent() {
return nativeIsTouchEvent(mNativePtr);
}
在dispatchPointerEvent方法中会有event.isTouchEvent()的判断,如果talkback模式下,由于收到的是ACTION_HOVER_ENTER事件,因此不会走dispatchTouchEvent方法而是dispatchGenericMotionEvent方法。
android.view.View.java
/**
* Dispatch a generic motion event.
* <p>
* Generic motion events with source class {@link InputDevice#SOURCE_CLASS_POINTER}
* are delivered to the view under the pointer. All other generic motion events are
* delivered to the focused view. Hover events are handled specially and are delivered
* to {@link #onHoverEvent(MotionEvent)}.
* </p>
*
* @param event The motion event to be dispatched.
* @return True if the event was handled by the view, false otherwise.
*/
public boolean dispatchGenericMotionEvent(MotionEvent event) {
...
final int source = event.getSource();
if ((source & InputDevice.SOURCE_CLASS_POINTER) != 0) {
final int action = event.getAction();
if (action == MotionEvent.ACTION_HOVER_ENTER
|| action == MotionEvent.ACTION_HOVER_MOVE
|| action == MotionEvent.ACTION_HOVER_EXIT) {
if (dispatchHoverEvent(event)) {
return true;
}
} else if (dispatchGenericPointerEvent(event)) {
return true;
}
} else if (dispatchGenericFocusedEvent(event)) {
return true;
}
...
return false;
}
在dispatchGenericMotionEvent中,如果是Hover events,则会走到dispatchHoverEvent方法中。这个方法的机制类似dispatchTouchEvent的流程,是一个责任链模式的实现,不详细展开,默认会传到最后一个子节点的onHoverEvent方法。接着该方法会调用到sendAccessibilityHoverEvent里。
3、sendAccessibilityHoverEvent方法接着会调用以下方法。
sendAccessibilityEvent
->sendAccessibilityEventUnchecked
->onInitializeAccessibilityEvent
->dispatchPopulateAccessibilityEvent
->onPopulateAccessibilityEvent
->onRequestSendAccessibilityEvent(只在ViewGroup中有默认实现)
*重要:以上六个方法为当我们自定义view时适配无障碍模式可以覆盖实现的方法,可以重写view的这些方法或者实现View.AccessibilityDelegate来解决一些特殊场景下talkback播报的问题。更详细的用法可以参考官方文档。
以talkback模式下朗读一个textview上的文字为例,textview重写了view中的onPopulateAccessibilityEventInternal方法
android.widget.TextView.java
/** @hide */
@Override
public void onPopulateAccessibilityEventInternal(AccessibilityEvent event) {
super.onPopulateAccessibilityEventInternal(event);
final CharSequence text = getTextForAccessibility();
if (!TextUtils.isEmpty(text)) {
event.getText().add(text);
}
}
getTextForAccessibility方法会取到当前textview中显示的text,然后将该text的内容填充到AccessibilityEvent中发送出去。后面talkback会取出这个text并朗读出来。
android.view.View
public void onPopulateAccessibilityEvent(AccessibilityEvent event) {
if (mAccessibilityDelegate != null) {
mAccessibilityDelegate.onPopulateAccessibilityEvent(this, event);
} else {
onPopulateAccessibilityEventInternal(event);
}
}
因此如果我们需要自定义textview在talkback模式下朗读的内容,或者不让某个view的内容在talkback模式下被朗读出来,可以考虑重写onPopulateAccessibilityEvent方法。
4、当我们通过第3步修改view中无障碍节点的信息后,被点击的View的sendAccessibilityEventUnchecked方法会向上通过DecorView传递到ViewRootImpl的requestSendAccessibilityEvent方法中,
android.view.ViewRootImpl
public boolean requestSendAccessibilityEvent(View child, AccessibilityEvent event) {
...
final int eventType = event.getEventType();
switch (eventType) {
case AccessibilityEvent.TYPE_VIEW_ACCESSIBILITY_FOCUSED: {
final long sourceNodeId = event.getSourceNodeId();
final int accessibilityViewId = AccessibilityNodeInfo.getAccessibilityViewId(
sourceNodeId);
View source = mView.findViewByAccessibilityId(accessibilityViewId);
if (source != null) {
AccessibilityNodeProvider provider = source.getAccessibilityNodeProvider();
if (provider != null) {
final int virtualNodeId = AccessibilityNodeInfo.getVirtualDescendantId(
sourceNodeId);
final AccessibilityNodeInfo node;
node = provider.createAccessibilityNodeInfo(virtualNodeId);
setAccessibilityFocus(source, node);
}
}
} break;
...
}
mAccessibilityManager.sendAccessibilityEvent(event);
return true;
}
接着无障碍事件会通过AccessibilityManager的sendAccessibilityEvent方法跨进程调用systemserver进程的AccessibilityManagerService,将类型为TYPE_VIEW_HOVER_ENTER的AccessibilityEvent事件传递到talkback的的TalkBackService(继承自AccessibilityService)的onAccessibilityEvent方法中(或者其他实现了AccessibilityService的应用)。
4.4、执行无障碍事件流程(以talkback发出focus无障碍事件,到被辅助的app端通过ViewRootImpl绘制绿框焦点过程进行分析)。
流程:辅助app(talkback)将无障碍事件发送给被辅助app,systemserver进程作为中转,接口为IAccessibilityServiceConnection.aidl和IAccessibilityInteractionConnection.aidl

分析该流程原因:
为了辅助理解如下方法:
AccessibilityNodeInfo.performAction
主要流程分析:
1、在talkback中有个AccessibilityEventProcessor类对无障碍事件进行集中处理,根据无障碍事件的不同类型分发到不同的处理器进行处理,比如ProcessorFocusAndSingleTap这个处理器会对类型为TYPE_VIEW_HOVER_ENTER的无障碍事件进行处理,ProcessorEventQueue(主要用于tts朗读,后面分析)这个处理器会处理所有的无障碍事件。
2、在前面一节4.2中,触摸事件TYPE_VIEW_HOVER_ENTER传递到了TalkBackService,而ProcessorFocusAndSingleTap这个类会对TYPE_VIEW_HOVER_ENTER这个事件进行处理,tryFocusing函数中会调用AccessibilityNodeInfo的performAction方法,AccessibilityNodeInfo的节点信息就是4.2节中触摸到的view的信息,因此通过AccessibilityManagerService进程中转后,会最终调用到我们触摸到的view的performAccessibilityAction方法中去(我们也可以通过调用这个方法处理一些无障碍焦点的问题)。
3、在performAccessibilityAction会调用到performAccessibilityActionInternal,接着如果判断到是ACTION_ACCESSIBILITY_FOCUS事件,则会调用requestAccessibilityFocus函数
android.view.View
public boolean requestAccessibilityFocus() {
...
if ((mPrivateFlags2 & PFLAG2_ACCESSIBILITY_FOCUSED) == 0) {
mPrivateFlags2 |= PFLAG2_ACCESSIBILITY_FOCUSED;
ViewRootImpl viewRootImpl = getViewRootImpl();
if (viewRootImpl != null) {
viewRootImpl.setAccessibilityFocus(this, null);
}
invalidate();
sendAccessibilityEvent(AccessibilityEvent.TYPE_VIEW_ACCESSIBILITY_FOCUSED);
return true;
}
return false;
}
这个函数里有两个重要的操作,一是调用ViewRootImpl的setAccessibilityFocus将自身设置为focus的view,然后调用invalidate触发重绘操作,ViewRootImpl会在onPostDraw中执行drawAccessibilityFocusedDrawableIfNeeded来绘制出绿框。
android.view.ViewRootImpl.java
/**
* We want to draw a highlight around the current accessibility focused.
* Since adding a style for all possible view is not a viable option we
* have this specialized drawing method.
*
* Note: We are doing this here to be able to draw the highlight for
* virtual views in addition to real ones.
*
* @param canvas The canvas on which to draw.
*/
private void drawAccessibilityFocusedDrawableIfNeeded(Canvas canvas) {
final Rect bounds = mAttachInfo.mTmpInvalRect;
if (getAccessibilityFocusedRect(bounds)) {
final Drawable drawable = getAccessibilityFocusedDrawable();
if (drawable != null) {
drawable.setBounds(bounds);
drawable.draw(canvas);
}
} else if (mAttachInfo.mAccessibilityFocusDrawable != null) {
mAttachInfo.mAccessibilityFocusDrawable.setBounds(0, 0, 0, 0);
}
}
private boolean getAccessibilityFocusedRect(Rect bounds) {
final AccessibilityManager manager = AccessibilityManager.getInstance(mView.mContext);
if (!manager.isEnabled() || !manager.isTouchExplorationEnabled()) {
return false;
}
final View host = mAccessibilityFocusedHost;
if (host == null || host.mAttachInfo == null) {
return false;
}
final AccessibilityNodeProvider provider = host.getAccessibilityNodeProvider();
if (provider == null) {
host.getBoundsOnScreen(bounds, true);
} else if (mAccessibilityFocusedVirtualView != null) {
mAccessibilityFocusedVirtualView.getBoundsInScreen(bounds);
} else {
return false;
}
// Transform the rect into window-relative coordinates.
final AttachInfo attachInfo = mAttachInfo;
bounds.offset(0, attachInfo.mViewRootImpl.mScrollY);
bounds.offset(-attachInfo.mWindowLeft, -attachInfo.mWindowTop);
if (!bounds.intersect(0, 0, attachInfo.mViewRootImpl.mWidth,
attachInfo.mViewRootImpl.mHeight)) {
// If no intersection, set bounds to empty.
bounds.setEmpty();
}
return !bounds.isEmpty();
}
第二个操作是调用sendAccessibilityEvent方法,将TYPE_VIEW_ACCESSIBILITY_FOCUSED事件发送出去,这个事件会被talkback处理,从而调用tts引擎读出view的内容,这个流程分析如下。
4.5、talkback调用TTS读出view中的text的过程。
由于talkback最新版本属于google维护,没有开源代码,网上公开的只有talkback6.0版本的代码,因此基于6.0版本的概要分析如下
无障碍事件的分发跟4.2节流程一样,talkback处理TYPE_VIEW_ACCESSIBILITY_FOCUSED事件大致流程如下:

talkback调用tts进行朗读主要通过com.google.android.accessibility.compositor.Compositor这个类来控制,这个类中又有一个ParseTree的类来管理朗读的内容,ParseTree通过一个compositor.json的文件来定义朗读的内容的规则,比如一个简单的按钮,在talkback模式下不仅需要读出按钮的内容,还需要读出按钮的状态(比如disabled),因此朗读的内容是一个拼接起来的结果,比如下面就是通过解析compositor.json来读出一个按钮内容的大概流程。
以下在compositor.json中某几个节点类型的定义,
$开头会被解析成ParseTreeVariableNode,比如 “node.text"经过ParseTreeVariableNode的处理会取出Button中text(也就是AccessibilityEvent中AccessibilityNodeInfo中的mText)
@开头会被解析成ParseTreeResourceNode,最后会通过Resource取出字段的内容,比如”@string/value_button"中文下会被解析为“按钮”,
“@string/value_disabled"中文下会被解析为“已停用”。
"notify_disabled": {
"if": "$node.isActionable && !$node.isEnabled",
"then": "@string/value_disabled"
},
....
"get_node_text": { // AccessibilityNodeInfoUtils.getNodeText()
"fallback": [
{
// If focusing on-screen keyboard key... apply speak-passwords policy to hide key name.
"if": "$event.sourceIsKeyboard && $global.lastTextEditIsPassword && !$global.speakPasswordOnAndroidShowingPasswords",
"then": "@string/symbol_bullet",
"else": "$node.contentDescription"
},
"$node.text"
]
},
"get_role_description_or_default": {
"fallback": [
"$node.roleDescription",
"%node_role"
]
},
"node_role": {
"switch": "$node.role",
"cases": {
"button": "@string/value_button",
"check_box": "@string/value_checkbox",
"drop_down_list": "@string/value_spinner",
"edit_text": "@string/value_edit_box",
"grid": "@string/value_gridview",
"image": "@string/value_image",
"image_button": "@string/value_button", // Same as |button|
"list": "@string/value_listview",
"pager": "@string/value_pager",
"progress_bar": "@string/value_progress_bar",
"radio_button": "@string/value_radio_button",
"seek_control": "@string/value_seek_bar",
"switch": "@string/value_switch",
"tab_bar": "@string/value_tabwidget",
"toggle_button": "@string/value_switch", // Same as |switch|
"view_group": "", // None
"web_view": "@string/value_webview",
"checked_text_view": "" // None
}
},
ttsOutput
TYPE_VIEW_ACCESSIBILITY_FOCUSED
get_description_for_tree
StateNameRolePosition
tree_description_with_label
append_description_for_tree
| “conditionalPrepend(%description_for_tree_status, %description_for_tree_nodes)”
| description_for_tree_nodes
| get_description_for_node
| rule_default
| node_text_and_role
| rule_view_group(%get_node_text)
| | “$node.text”———–取出“Button的text”
| get_role_description_or_default
| | %node_role————-取出“按钮的String资源”
notify_disabled————-取出“已停用的String资源”
最后talkback朗读“xxx,按钮,已停用”